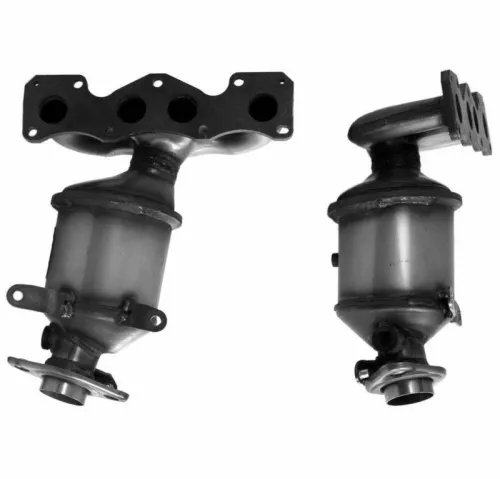
AHG AHG92587 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9505844598146
AHG AHG92587 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9505844598146
Product number: AHG92587
EAN: 9505844598146
EAN: 9505844598146
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92586 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9507281817866
AHG AHG92586 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9507281817866
Product number: AHG92586
EAN: 9507281817866
EAN: 9507281817866
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92585 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503861866941
AHG AHG92585 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503861866941
Product number: AHG92585
EAN: 9503861866941
EAN: 9503861866941
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92551 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9507562315692
AHG AHG92551 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9507562315692
Product number: AHG92551
EAN: 9507562315692
EAN: 9507562315692
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92550 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9501146626297
AHG AHG92550 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9501146626297
Product number: AHG92550
EAN: 9501146626297
EAN: 9501146626297
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92497 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9506652386994
AHG AHG92497 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9506652386994
Product number: AHG92497
EAN: 9506652386994
EAN: 9506652386994
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92478 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9507343129180
AHG AHG92478 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9507343129180
Product number: AHG92478
EAN: 9507343129180
EAN: 9507343129180
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92475 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503959593315
AHG AHG92475 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503959593315
Product number: AHG92475
EAN: 9503959593315
EAN: 9503959593315
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92472 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9501772911552
AHG AHG92472 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9501772911552
Product number: AHG92472
EAN: 9501772911552
EAN: 9501772911552
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92469 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9505482576698
AHG AHG92469 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9505482576698
Product number: AHG92469
EAN: 9505482576698
EAN: 9505482576698
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92467 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9505135351696
AHG AHG92467 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9505135351696
Product number: AHG92467
EAN: 9505135351696
EAN: 9505135351696
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92451 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9504354291936
AHG AHG92451 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9504354291936
Product number: AHG92451
EAN: 9504354291936
EAN: 9504354291936
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92432 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9502922693298
AHG AHG92432 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9502922693298
Product number: AHG92432
EAN: 9502922693298
EAN: 9502922693298
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92431 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503337538631
AHG AHG92431 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503337538631
Product number: AHG92431
EAN: 9503337538631
EAN: 9503337538631
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92417 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9508617259374
AHG AHG92417 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9508617259374
Product number: AHG92417
EAN: 9508617259374
EAN: 9508617259374
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92406 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503519351768
AHG AHG92406 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503519351768
Product number: AHG92406
EAN: 9503519351768
EAN: 9503519351768
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92394 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503613134465
AHG AHG92394 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9503613134465
Product number: AHG92394
EAN: 9503613134465
EAN: 9503613134465
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer
AHG AHG92392 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9509126262381
AHG AHG92392 Catalytic Converter
EAN: 9509126262381
Product number: AHG92392
EAN: 9509126262381
EAN: 9509126262381
To see the prices, you need to login or become a customer

Catalyst
##AFFIL_SHOPNAME## offers you a wide range in beautiful and luxurious Catalyst. We have Catalyst in various styles such as metropolitan, modern, rural or luxurious. We have a matching Catalyst for every living style and taste.